Apr 23, 2025
Tamara J. & Brian
7min Read
A web server stores and delivers files to browsers, making your site accessible to users. It also processes files for emails and data storage using Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
While it’s possible to set up your own server, renting it from a web hosting provider saves you time, money, and effort. Keep reading this article to learn how web servers work, why they’re important, and some of the popular examples.
Download glossary for web beginners
A web server is a computer that hosts web pages, making them accessible online. When a user loads a site, the web server will retrieve the relevant files and send them to the browser so the user can interact with them.
Let’s break down the main components of a web server:
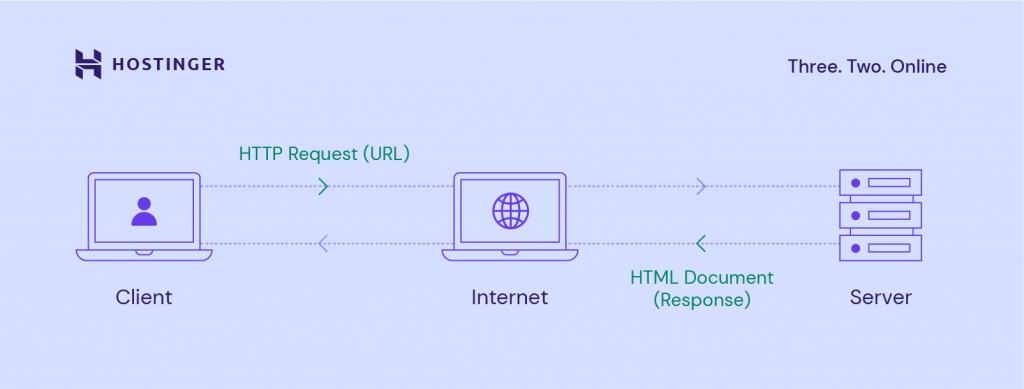
Web and application servers follow a client-server model. In this structure, one program – the client – requests a resource or service from another program – the server.
Web servers use Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) when responding to user requests via the World Wide Web. HTTP is a protocol used to exchange information between computers.
Through the HTTP request process, servers can deliver the site’s HTML document to the user’s web browser, like Google Chrome.
Here’s an overview of the whole process to give you a better understanding:
When the HTTP server fails to find or process the requested files, it will send an HTTP error status code to the browser.
The most common error message is a 404 error, which means the requested page is missing. Meanwhile, a 403 error may appear if there are permission issues.
Furthermore, if a web server fails to receive a timely response from another server acting as a proxy or gateway, a 504 error occurs.
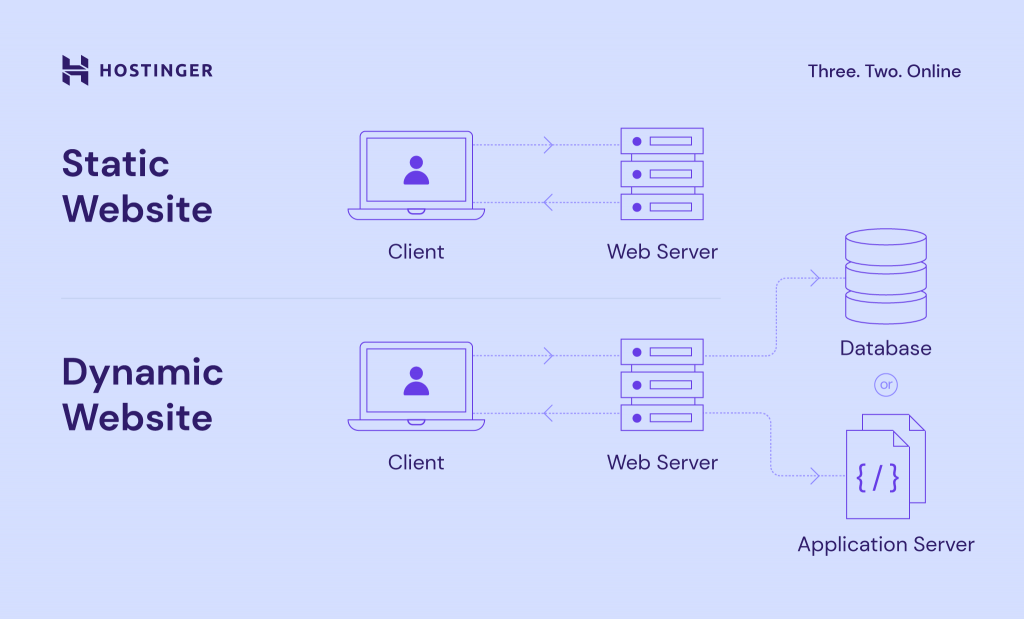
Web servers can generate both static and dynamic content depending on the installed software.
Static web servers comprise a computer and HTTP software. Meanwhile, a dynamic web server consists of a static web server plus extra software, commonly an application server and databases.
A static web server sends files to web browsers without any changes, making them suitable for sites with fixed content like blogs and portfolios. Since there’s no need for complex server-side processing, static websites tend to load faster.
On the other hand, a web server for a dynamic website updates hosted files using additional software to personalize content based on user interactions. It’s the perfect option for sites like social media platforms and eCommerce stores.
For instance, when a visitor purchases a product, the dynamic site’s algorithm will recommend similar items in the same category on their next visit.
Web servers can handle multiple tasks, such as sending and receiving emails, storing web applications, and processing FTP requests. However, the primary use of a web server is to host websites, making them functional and interactive for users worldwide.
To create and publish a website, you need access to a web server. The easiest way to accomplish this is by purchasing web hosting and a domain name from a hosting provider.
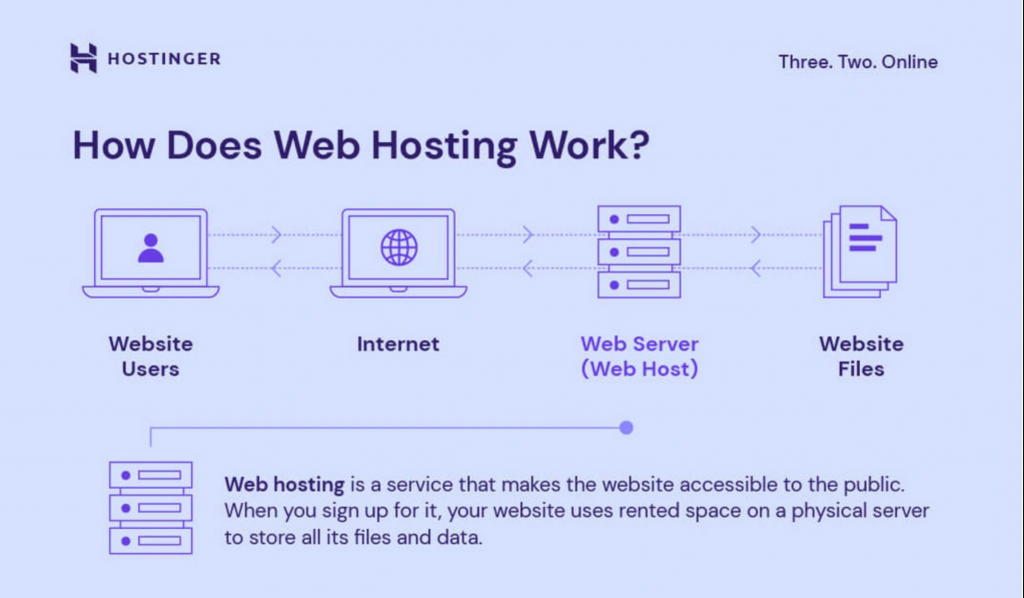
Website hosting services provide your website with server space to store its files and databases. Meanwhile, a domain name acts as a unique address for your website, helping visitors find it easily.
Learn everything you need to know about web hosting and domain names in these comprehensive guides:
What Is Web Hosting – Web Hosting Explained for Beginners
What Is a Domain Name? A Beginner-Friendly Guide
To ensure web server security and performance, the web hosting provider will perform regular maintenance. That’s why choosing a reliable web hosting provider is crucial. Other benefits of having a trusted web host include:
Aside from processing incoming browser requests and responses, most web servers also offer the following features:
Looking for ways to boost your web server performance? Check out this tutorial on how to monitor website uptime and prevent downtime.
Some of the most common web servers include:
Web hosting companies support different types of servers. For example, Hostinger VPS supports Apache and NGINX, the two leading web servers in the market.
Learn how to set up an NGINX reverse proxy with our comprehensive guide.
The way a web server is configured greatly influences its reliability and security. To ensure the best performance, server administrators carry out several tasks:
At Hostinger, our web servers are protected by advanced DDoS countermeasures and an AI-powered firewall. This allows us to provide a secure and highly responsive hosting environment.
For maximum speed, we use the latest technologies like NVMe SSD storage and AMD EPYC processors running on industry-leading HPE and DELL server hardware. Plus, our data centers are strategically located across four continents.
Hostinger’s blend of cutting-edge hardware, advanced security measures, and globally-spread data centers helps us offer a 99.9% uptime guarantee and unbeatable performance.

A web server connects your website to the internet. It consists of hardware and software, each playing a distinct role in processing files.
The primary function of a web server is to host websites, process HTTP requests, and deliver web content to users. Besides Apache and NGINX, other web servers in the market include Microsoft Internet Information Services and Lighttpd.
Different types of web servers can deliver dynamic content or static content to a browser. A static website displays the same content to everyone, while a dynamic website shows content that’s unique to each user.
Purchasing a web hosting plan is necessary for any website type. The web host will be responsible for maintaining the server’s security and performance. This way, you’ll have more time to focus on other matters, such as your business’s marketing and day-to-day operation.
Find answers to commonly asked questions about a web server.
A web server primarily responds to HTTP requests by delivering static content like web pages and images to a browser. Meanwhile, an application server is responsible for executing dynamic tasks, such as running scripts, processing forms, and interacting with databases to deliver interactive web applications.
A web server consists of hardware and software. The hardware side connects to the internet to exchange data, and the software side includes an HTTP server that processes requests and URLs. Together, these web server components make websites, apps, and files accessible across the internet.
When choosing a web server, consider factors like the server’s performance, security features, compatibility with your website’s tech stack, ease of management, support options, and pricing. You can start with Hostinger’s shared server hosting before upgrading to VPS or cloud-based solutions for better performance.
Some popular web servers for small businesses are Apache HTTP Server, NGINX, and Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS). These servers are highly reliable and widely used. The best choice will depend on your specific needs and the technologies your website uses.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.